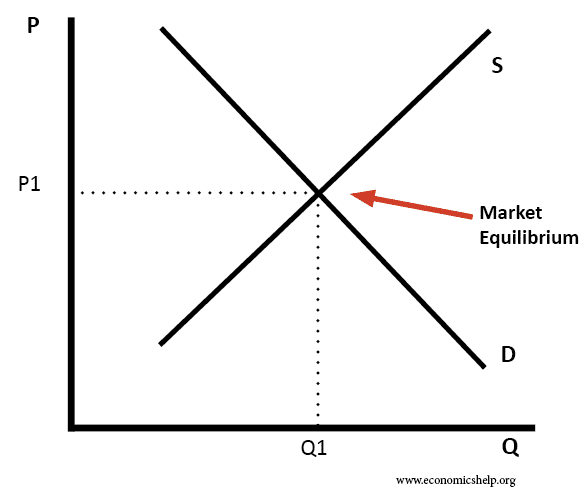
Normal profit
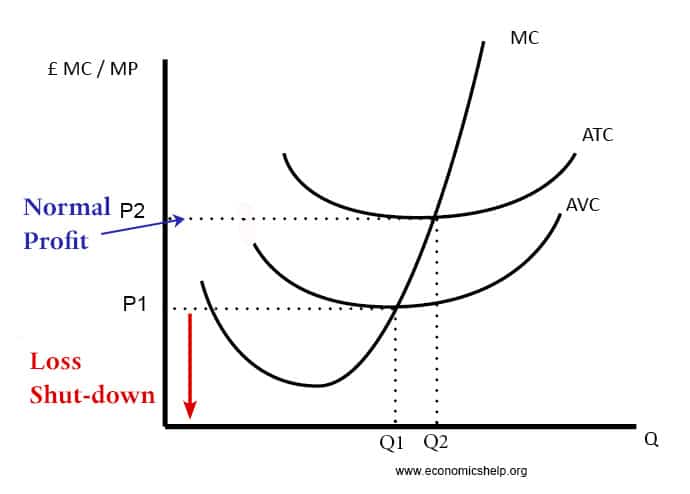
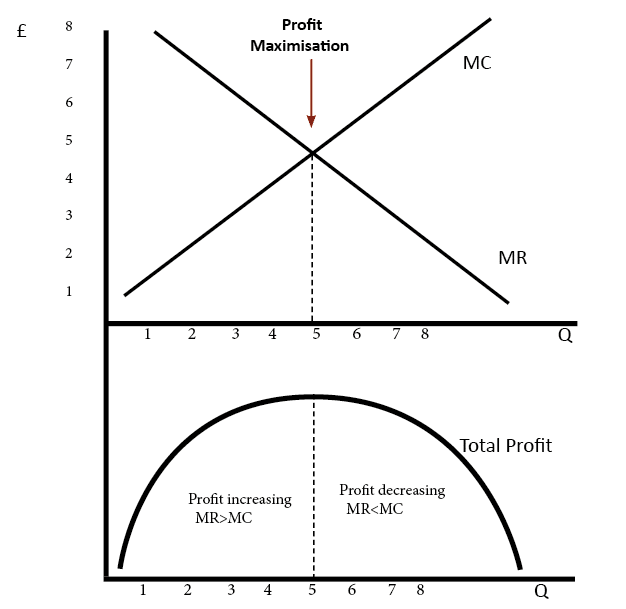
Normal profit is a situation where a firm makes sufficient revenue to cover its total costs and remain competitive in an industry. In measuring normal profit, we include the opportunity cost of working elsewhere. When a firm makes normal profit we say the economic profit is zero. Normal profit = total revenue – total costs …